Learning Outcomes From This Post
- Learn Life Cycle Analysis Phases and Circular Economy.
- Understanding the benefits and key steps to Life Cycle Impact
- Analysis and Life Cycle Cost Analysis and what can be used for the studies.
- Importance of Integration between Life Cycle Impact Analysis and Life Cycle Cost Analysis
- How Architects/Designers can proactively integrate these methods in building design.
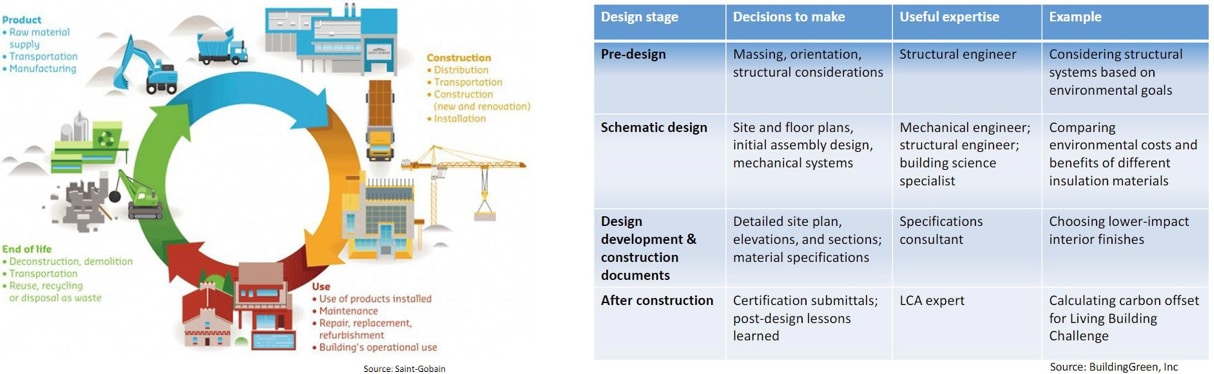
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA)
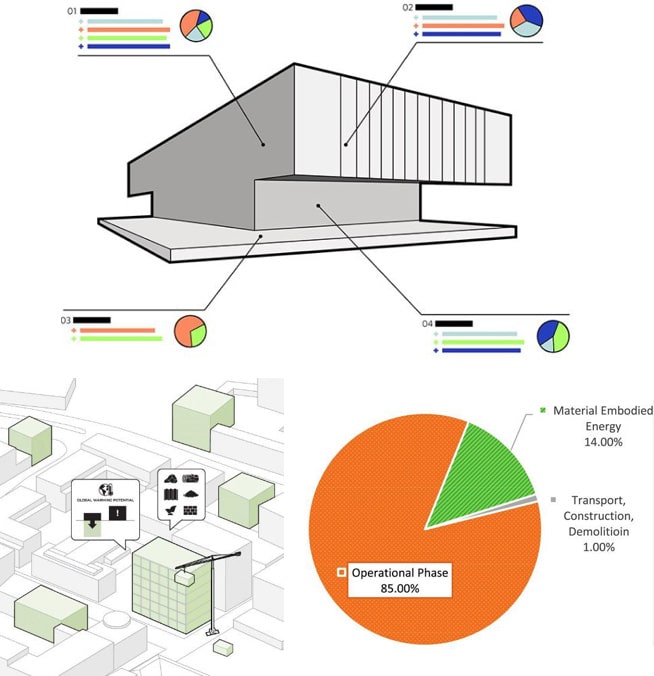
- Life Cycle Analysis can offer insight on how a building will perform.
- A technique to assess environmental impacts and potential impacts associated with a product.
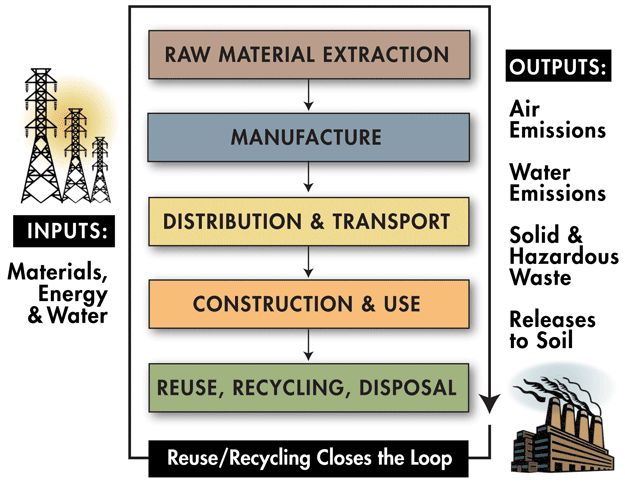
- LCA concepts include Cradle-to-Gate, Cradle-to-Grave, Cradle-to-Cradle, Embodied Carbon/Energy/Water, Global Warming Potential (GWP).
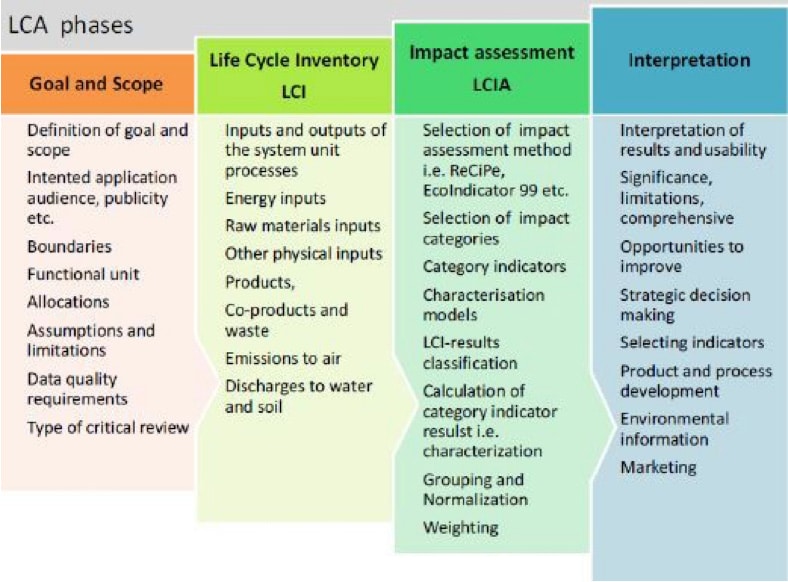
Life Cycle Analysis Phases
Goal and scope: Determining the scope of analysis.
(e.g., Entire building, structural components, finishes, or mechanical systems.)
Life Cycle Inventory: What goes into a material and what comes from it.
(e.g., raw resources and emissions)
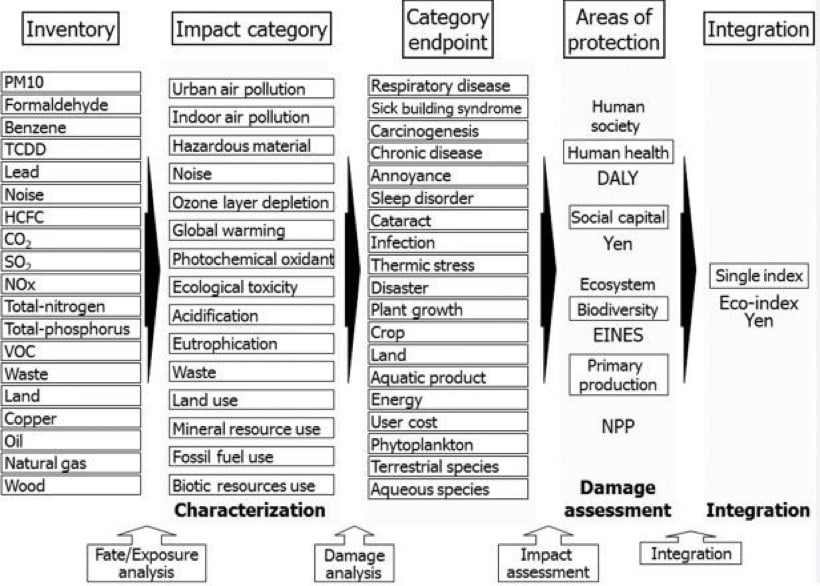
Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA)
- Evaluates environmental, social, and economic impacts for a project (or product) through its life cycle. This is important to make sustainable design decisions.
Benefits of LCIA
- Enables a comprehensive environmental and social assessment
- Identifies hotspots for improvements
- Influences environmentally conscious design decisions
- Enhances project reputation and marketability
LCIA Key Steps
Key steps include:
- Inventory Analysis
- Impact Category Selection
- Characterization
- Normalization
- Weighting
- Interpretation
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Reporting
Life Cycle Cost Analysis (LCCA)
Assesses costs associated with a project/product over its entire life cycle
LCCA Steps:
- Cost Identification
- Cost Estimation
- Discounting
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Interpretation Benefits of LCCA
Influences cost-effective design choices:
- Considers all costs, not exclusive to initial cost
- Supports budgeting and investment decisions
- Enhances financial planning and project feasibility
Programs
Life Cycle Impact Analysis
Honorable Mentions: Tally, EQUER, Green Building Studio, EcoImpact-COMPASS, ISES-CEE, Life Cycle Assessment in Buildings (LCA-IB), Building for Environmental and Economic Sustainability (BEES), and Building Industry Reporting Design for Sustainability (BIRDS)
Life Cycle Cost Analysis
Honorable Mentions: eQuest, PlanIt Impact, BIM 360, ARCHIBUS, BuildingOS, SEED Platform, EnergyPlus, and Green Building Studio
Interpretation
Analyze and understand results in order to translate them into actionable insights for decision-making.
These steps can include:
- Analyze Results
- Hotspot Identification
- Comparative Analysis
- Risk/Uncertainty Assessment
- Prioritization
- Strategic Decision Making
- Trade-Offs
- Communication
- Feedback Loop
- Continuous Improvement
Effectively communicating this step will require more than presenting numbers and data, but to show an understanding of environmental and social impacts, enabling smart decision making for a building project.
Integration of LCIA and LCCA
- Importance of combining both methodologies
- Achieving holistic sustainable design
- Balance between environmental impact and cost considerations
How Should Architects and Designers Integrate Life Cycle Analysis?
- As early as possible integration in the design process
- Collaboration with experts
- Consideration of alternative materials, energy sources, and technologies
- Regular reassessment and improvement throughout life cycle process
Conclusion
- Life Cycle Analysis is a method to offer insight on how a building will perform.
- Life Cycle Impact Assessment looks at the natural resources that go into a “product” as well as the output.
- Life Cycle Cost Assessment will detail the types of costs that are within the building project, more in-depth than just “initial costs”
- Architects and Designers should utilize an “Integrative Design Process” that gathers all pertinent members of a project in order to efficiently design a sustainable building. (Ex. Architects/Designers, Consultants, Stakeholders, Occupants, and Trade Professionals)